Islamic finance is a means of carrying out transactions and banking operations in accordance with Islamic law or Sharia law. Islamic finance is a $2.5 billion industry, present in more than 80 countries.1 Islamic financial institutions help mobilize private savings for public sector infrastructure projects that can bring in profits on a profit-sharing basis, such as tolling for highway use. Some infrastructure projects built by the private sector for the government can be purchased in anticipation of returns.
Sukuk and Musaka
A Sukuk is a kind of Islamic bond (unlike Western bonds, interest payments are not allowed under Sharia law), in which the issuer of a Sukuk sells a certificate and uses the proceeds of the sale to buy an asset in which the group of investors has a direct partial interest. The issuer enters into an agreement to redeem the bond at a later date than its face value.
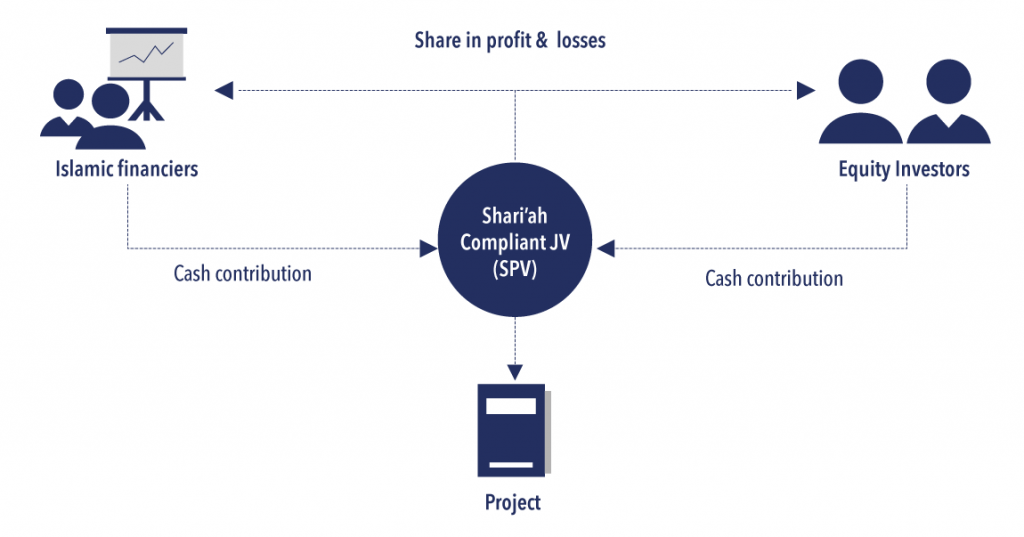
The Musakah is a joint partnership agreement in Islamic finance in which profits and losses are shared. Since interest gains are not allowed, a permanent musaka is often used for long-term financing, as it has no specific end date and continues until the partners decide to dissolve it, like equity partners in a company. 2
The structure of the Musaka
Volumes of Sukuks in Africa
The Sukuk and Mushaka would be excellent instruments to finance infrastructure (designed as PPPs).
Islamic financing instruments can be particularly suitable for infrastructure development, as they are an asset-based system based on risk-sharing in halal or licit activities, rather than on interest gains. In addition, the high degree of transparency they offer provides an incentive to monitor infrastructure projects and improve the efficiency of project construction and operation. 3
For infrastructure PPP projects, a musaka structure (with a financial institution and capital investors) would be ideal as both parties remain invested and share the profits and losses of the project. For example, the government can provide the land needed for infrastructure, while the private sector can provide capital and construction support. The ongoing partnership in this structure mitigates the project risk to infrastructure PPPs.
Sukuk has become an essential instrument for mobilizing medium- and long-term capital in Africa. With the growth of sustainable infrastructure in Africa, Sukuk as a fundraising tool is increasingly used by investment funds, in particular because of their viability and dynamism.
Islamic finance has growth potential, as it can support sustainable development through PPPs and positive socio-economic outcomes.6
- https:llwww.soundvision.comlarticlelfinancing-infrastructure-building-role-of-islamic-financial-institutions
- Worldbank documents
- https:llwww.islamicfinance.coml2018l02lsukuk-issuance-africa-prospect-growthl
- https:llblogs.worldbank.orglvoiceslhow-islamic-finance-can-boost-infrastructure-development

